Chronic diseases are long-term health concerns that last for a minimum of 3 months and generally progress as it gets much over time. Chronic diseases are a matter of significant concern as they severely impact a person's life. These diseases are complex and require proper management plans and a high level of medical attention.
Approximately 21% of the elderly population in India reportedly suffer from at least one chronic disease. Not just that, but they are also the leading cause of global health problems, affecting millions of people worldwide. This highlights the impact of these conditions and underscores the importance of early detection and effective management. This blog has explored the ten most common chronic diseases, their symptoms, and management techniques.
Heart disease
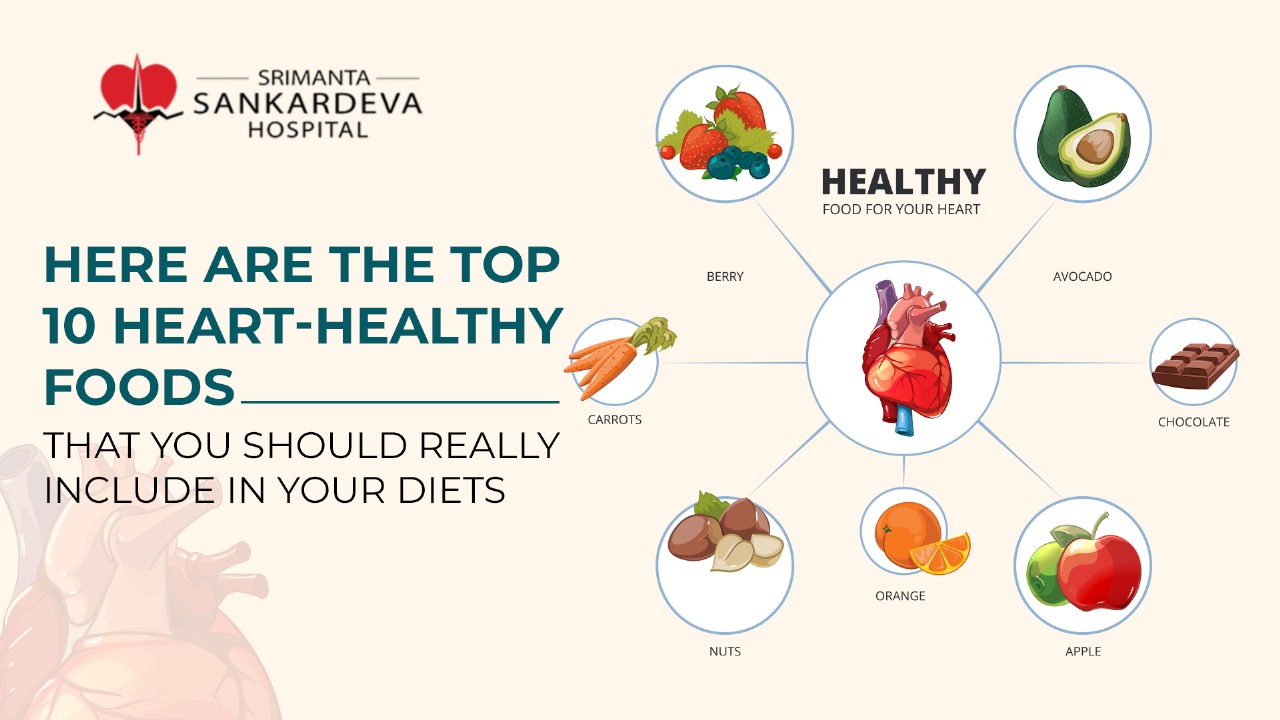
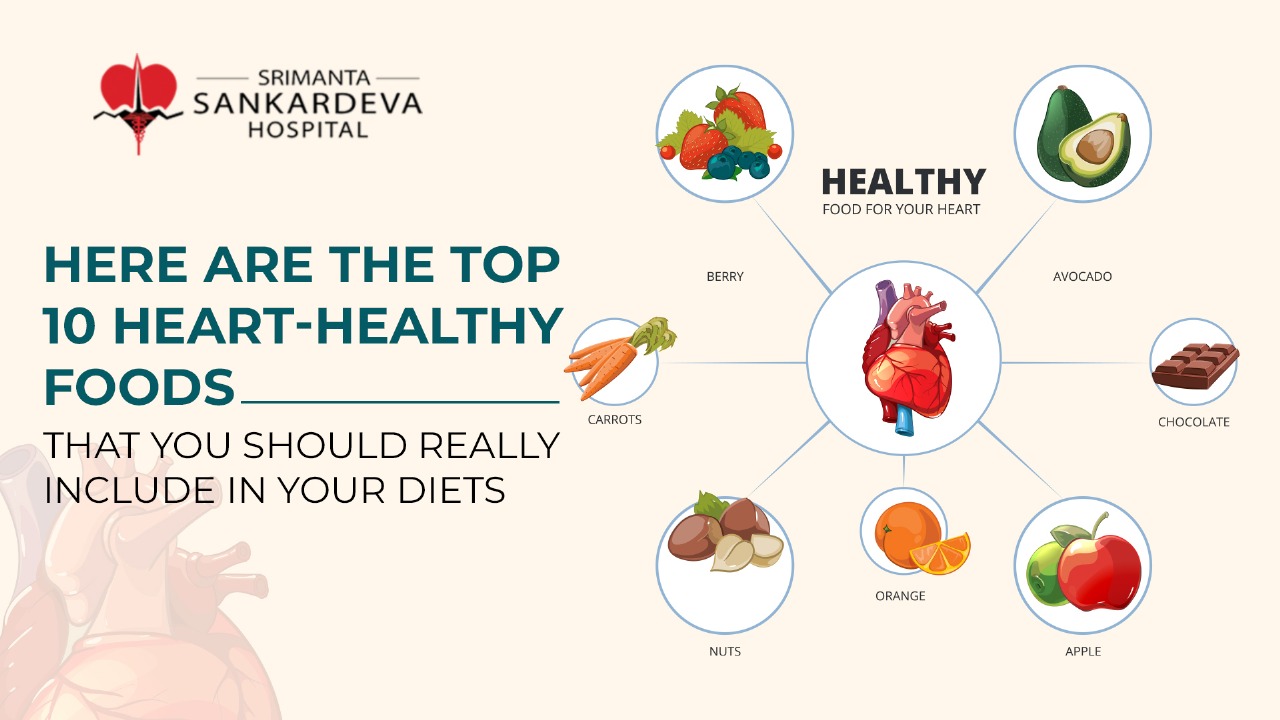
Heart diseases are the most prevalent chronic illnesses, affecting millions of people worldwide. The common symptoms of heart disease include a combination of signs such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and extreme fatigue, pain in the neck, upper belly or jaw, and numbness in arms or legs.
Heart diseases require to be appropriately managed by adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular activity, and quitting activities like smoking. At the same time, taking medicines as prescribed by the doctor to regulate cholesterol and blood pressure is essential. If you have a family history of such heart diseases, it is necessary to visit the doctor to ensure early detection and risk the progression of the heart disease.
Cancer
Cancer is one of the most common chronic conditions, with millions of people getting diagnosed every year. The symptoms of cancer are varied and depend on the type of cancer a person is suffering from. Some of the common symptoms include sudden and unexplained weight and extreme fatigue. There is not one set treatment plan when it comes to treating cancers. Therefore, it is essential to visit the top specialist to get the best recommendation as they walk you through the first treatment option suited for you.
Treatment options like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy are generally prescribed to patients. If there is a family history of cancer, it is advisable to go to regular screenings as early detection plays a significant role in managing and treating cancer effectively.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic disorder that occurs when the pancreas in your body cannot produce enough insulin or is unable to use it as required by the body. It can also happen when the body fails to respond to the insulin being produced. The most common types of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2, as well as gestational diabetes.
Type 1 is a chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
Type 2: It is a chronic condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin being produced or, in other cases, occurs when there is not enough.
Gestational diabetes:
This develops during pregnancy, and generally goes away with time. Proper monitoring of the patient needs to be done to prevent it from developing into type 2 diabetes.
Some common symptoms include having excessive thirst, bouts of extreme fatigue, frequent urination, along with blurred vision. Visiting an expert who shall help manage your chronic condition is essential. Your doctor shall ask you to consume a healthy diet and indulge in regular exercise, medications, and insulin therapy. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is the best path forward to reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Chronic respiratory diseases
Chronic respiratory diseases, such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and asthma, are among the most common chronic diseases worldwide. These conditions cause breathing difficulties, wheezing, and coughing. COPD is often caused by smoking, while allergens and environmental factors can trigger asthma. Managing chronic respiratory diseases involves using inhalers, avoiding triggers, regular exercise, and, in severe cases, oxygen therapy.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease is a progressive condition where the kidneys gradually start losing their ability to filter waste from the blood. Advanced chronic kidney disease can lead to harmful buildup of fluids, electrolytes, and waste in the body. There are often fewer symptoms in the early stages, making it easier to detect once the disease progresses. Signs of chronic kidney disease develop over time if kidney damage progresses slowly.
But this does not mean there are no subtle signs. These include swelling in the legs, fatigue, and changes in urination. Long-term effects of CKD include an increased risk of heart disease and kidney failure. Managing CKD involves controlling blood pressure, maintaining a low-sodium diet, and monitoring blood sugar levels. In severe cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be necessary.
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease is a brain condition that affects the memory and thinking of a person, leading to significant changes in their behaviour. It is characterised by changes in the brain that deposit certain types of protein. Alzheimer's degenerative disease is the most common chronic condition in older adults. Alzheimer's is the most common cause of dementia. According to statistics, 8.8 Indians aged 60 and above are living with dementia.
The early signs of Alzheimer's disease include forgetting recent conversations and events, difficulty in concentration, confusion about the day, time and place. But, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience difficulty in day-to-day communications, frequent mood swings, and loss of ability to do simple tasks on their own.
The sad truth is that there is no cure for this condition, but proper medication over a long period might help in slowing the progression of the condition. Patients might also enrol in therapies and programs designed to help manage their symptoms and ensure a better quality of life.
Arthritis
Arthritis a is a chronic condition that affects the joints, resulting in extreme pain, swelling and stiffness. There are many different causes of arthritis, each with different causes and treatment procedures.
The most common types are osteoarthritis, which results from wear and tear and generally affecting older people. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the healthy joint tissues. Gout is another common condition characterised by severe pain, often caused by excessive uric acid buildup.
The common symptoms of arthritis include redness, extreme pain, and swelling of the joints. This causes difficulty in moving and being able to do daily tasks.
Treatments for arthritis include pain management, physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle changes. Moreover, regular exercise and a healthy diet shall help in reducing inflammation.
Hypertension
According to the World Health Organization, hypertension is a significant cause of premature death worldwide. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a chronic disease that increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. It happens when the pressure in your blood is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher).
Hypertension is often dubbed the "silent killer", as the symptoms do not even start showing until the condition has advanced, leading to disastrous complications.
Symptoms of hypertension include severe headaches, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, nosebleeds among others. If you are experiencing such symptoms, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Managing hypertension involves:
-
Lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake.
-
Partaking in proper physical activity.
-
Maintaining a healthy weight.
-
Taking prescribed medications to control blood pressure levels.
Obesity
Obesity is a chronic condition characterised by excessive body fat, leading to an increased risk of other chronic illnesses, such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
The causes of obesity include a combination of poor diet, lack of exercise, and certain medications like antidepressants. Also, a person's genetics plays a role in influencing the cause of obesity.
Managing obesity requires a comprehensive approach to eating healthier and regular physical activity. One can also opt for counselling sessions to help you navigate the process better.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted, leading to sudden bleeding in the brain. A stroke requires immediate medical intervention, as not seeking proper medical attention at the right time can lead to long-term disability and even death. The common symptoms include sudden numbness, confusion, slurred speech, loss of coordination, sudden headache with no known cause, and dizziness or loss of balance. Managing stroke risk involves:
-
Controlling a spectrum of things like managing blood pressure following a healthy diet.
-
Engaging in regular exercise.
-
Avoiding smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol.
Conclusion: Managing Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases require proper management and intervention at the right time. Therefore, knowing the different conditions is crucial as it shall allow you to identify if you or your loved one is suffering from the early stages of a condition. This shall enable you to seek early medical care that might prevent long-standing complications, and you can take proactive steps towards better health and overall well-being.